
Prodigy Finance Brings the Most Accessible Education Loans - A Great Alternative to Traditional Student Funding

How to Get into a Top Engineering College in the United States and Qualify for an Education Loan

Bholaa Box Office Collection Day 16: Ajay Devgn’s Has Gain A Minor Growth on 3rd Week

Shaakuntalam Box Office Collection Day 1: Samantha’s Film Opened Generously At The Theatres

Shaakuntalam Movie Review: Samantha’s act is upto the mark, though received mixed reviews

Bloody Daddy: OTT Release Date, OTT Platform Star Cast, Storyline, Teaser, Trailer & More Details.

Bholaa Box Office Collection Day 16: Ajay Devgn’s Has Gain A Minor Growth on 3rd Week

Shaakuntalam Box Office Collection Day 1: Samantha’s Film Opened Generously At The Theatres

Bloody Daddy: OTT Release Date, OTT Platform Star Cast, Storyline, Teaser, Trailer & More Details.

Gumraah: OTT Release Date, Time, Stars, Plot, OTT Platform, Digital Rights

Gumraah Box Office Collection Day 5: Aditya Roy Kapur-Mrunal Film’s Minted Just Rs 70 Lakhs

Bholaa Box Office Collection Day 13: Ajay Devgn’s Film Keeps On Declining Each Day

Smartphone Features That Have Seen Significant Developments

Skill gaming company OpenPlay joins ‘Friends of Nazara’ network after ₹186 crore acquisition

Upcoming 5G Phones in India: List Of Upcoming 5G mobiles In 2021

Top Mobiles To Be Launched In September 2021: Smartphones Releasing In September 2021

iPhone 13 Launch Price In India, Launch Date, Specifications, Leaks & More

Foldable iPhone: Apple's clamshell-like folding iPhone is in early stage, Reports

Winter Skincare Routine: 5 Tips to keep your skin healthy and shiny that everyone should follow

Skincare tips: These 5 things will help you to get 'naturally glowing' skin instantly

Raksha Bandhan 2020 Mehndi Designs: This Rakhi apply easy and latest mehendi designs at home

Hariyali Teej 2020: Latest & Easy Mehndi Designs for Sawan Teej festival

Eid-Ul-Fittr Arabic Mehandi Designs| Apply these Eid 2020 Special designs try even at home

IGNOU Assignment Status 2022: Check TEE June 2021 Assignment Marks at ignou.ac.in

NEET PG 2022 Registration Starts @nbe.edu.in; Exam on March 12, Check Details

PPC 2022 Registration Closing On 20 January, Check Pariksha Pe Charcha Eligibility, Gifts & Registration Process

Delhi Govt Announces Special Yoga Classes for COVID Patients, Link To Activate Today, 1st Batch From Tomorrow, Details

DDMA Guidelines Released, All Private Offices Shall be Closed, Takeaways From Restaurants, Jan 11 Notification Here

GITAM Result 2021 Out For BTech & B.Pharmacy Semester Exams @gitam.edu; Check Notification Here

Happy Children's Day 2022: Quotes, Images, Wishes, Greetings, Messages, Texts & More

Guru Nanak Jayanti 2022: Images, Quotes, Wishes, Greetings, Messages To Share On Gurpurab 2022

Guru Nanak Jayanti 2022: Facts, History, Significance, & More About Gurpurab 2022

Happy Chhath Puja 2022: Quotes, Wishes, Messages, Images, Greetings & More

Happy Bhai Dooj 2022: Greetings, Wishes, Quotes, Images, Messages, WhatsApp Status & More

Bhaiya Dooj 2022: History, Date, Time, Significance, & More About The Auspicious Day

ISRO Chief K Sivan honoured with Von Karman Award 2020

How to Check Aadhar Card Status Online in Mobile? Download Using Update EID & Mobile No

China reveals detail of the pandemic, deny all allegations of covering outbreak

Coronavirus is likely to become a seasonal infection like the flu, top Chinese scientists warn the world

Chhattisgarh Engineering student develops Doctor Robot, to interact with Corona patients

How to Update Data in Aadhar Card Change Address, Mobile Number

Bargaining gain for China, CPEC less likely to serve Pakistani interests

Pak MP marries 14-year-old girl from Balochistan, police launches investigation

Pakistan Army launches operation in Balochistan, kills two locals and abducts women and children

Norwegian Intelligence agency enlists Pakistan as threat to its internal security: Report

Stone pelting at Pakistani high court, Judge besieged by protestors for more than 1 hour.

Another surgical strike inside Pakistan, Iran rescues its abducted soldiers from Balochistan

World Health Day 2023: Date, History, Key Facts, Significance, Celebration & More

World Kidney Day 2022: History, Significance, Celebration & More Details

Top 20 Monday Motivational Quotes - Best Monday Motivational Quotes inspirational thoughts to start your week

Five Home Remedies to lose weight in just 20 days without doing any exercise

World Chocolate Day 2020: Know about history of Chocolate & its benefits

International Yoga Day 2020: Theme, Significance & History

BAMU Result 2021 Declared @ bamua.digitaluniversity.ac; Check BA, BCom & BSc Sem 1 & 2 Results Here

Homi Bhabha Exam Result 2022 Declared at msta.in, Link to Check Class 6, 9 Results Here

ICSI Result 2021; CS Foundation & CSEET Dec 2021 Results Out Tomorrow at icsi.edu

Calicut University Results 2021 Declared at results.uoc.ac.in, Check M.Sc Semester 1, 3 & 4 Results Here

XAT Result 2022 Announced, Link Activated at xatonline.in & Removed, Check What's Going On

RRB NTPC Result 2021 Declared, Check Zone-Wise Results (Level 2-6) & CBT 1 Cut off Here

Saas, Bahu Aur Flamingo: OTT Release Date, Time, Starcast, Plot, Trailer, Streaming Details & More

Jubilee- OTT Web series, OTT Release Date, OTT Platform, Time, Genre, Star Cast, Teaser, Trailer, Plot & More

Beast Of Bangalore Review: A Gruesome And Heart Wrenching Tale Of Crime & Criminal

Jack Ryan Season 3: OTT Release Date, Trailer, Where To Watch, Star Cast & Plot

Emily in Paris Season 3: Release Date, OTT Platform, Cast, Trailer, Story & More

Girls Hostel Season 3 Review- Worth Investing in the Friendship, Though It’s a One-Time Watch

Passenger Plane scorched with fire at an airport in Saudi Arabia by Houthi rebels

Iran conducts Surgical strike inside Pakistan, freed two of its soldiers in an Intelligence-based Operation

Military Coup in Myanmar: State Counsellor Suu Kyi and President Myint sent to two weeks' remand

Myanmar Army seizes power, imposes 1 year emergency, president arrested

Nepal Protests: Police use water cannons to disperse the protesters from restricted zone

Iran Foreign Minister lashes-out at USA hours after Joe Biden sworn as 46th US President

Dassault Aviation's French billionaire Olivier Dassault died in a Helicopter crash

Israel claims of Covid19 injection, to kill virus inside body, said Def Minister

Happy Birthday Karl Marx: German Philosopher turns 202

Countries lifting lockdown- Italy, US, Germany, UK, Spain prepared roadmap to ease restrictions

Oxford University to conduct Coronavirus Vaccine Human Testing Trials today

WHO Chief replied Trump over allegations- to stop deaths US-China should work together

Bigg Boss 16 Contestants List: List of Contestants That Will Take Part In Bigg Boss 2022

Celebrities React To Arvind Trivedi's Death: Here's How The Showbiz Industry Reacted

Arvind Trivedi Death Reason: Know How The 'Ravana' Of Ramayan Died

The Kapil Sharma Show In Trouble: FIR Registered Against The Kapil Sharma Show

Latest TV Twists in Top 5 TV Serials List: Find How What's Happening In The World Of TV Serials

Bigg Boss 15 Contestants List: Punjabi Singer Afsana Khan To Enter The House

Merry Christmas 2022: Wishes, Quotes, Messages, Greetings & Images To Share On Christmas

Holi 2022: History, Significance and celebration

Chhath Puja 2020: Know date, time, Puja rituals, images, and significance of the festival

Happy Chhath Puja 2020: Wishes, Images, Quotes, Messages, and GIF Videos

Chhath Puja 2020 Date: Know the Sunrise, Sunset and Muhurat Timing

Bhai Dooj 2020: Know date, time, wishes, quotes, images, and significance of the festival

RPSC SI Physical Admit Card 2022 Out, Download Using SSO Id at rpsc.rajasthan.gov.in

RUHS B.Sc Nursing Admit Card 2022 Out at ruhsraj.org, Exam on 25 January

OSSC Group C Admit Card 2022 Out at osssc.gov.in, Login to Download, Exam on 30 Jan

AP SBTET Diploma Hall Ticket 2022 Released at apsbtet.net, Know How To Download

inter22.biharboardonline.com Admit Card 2022 Out, Know How To Download Bihar Board 12th Admit Cards

GATE Admit Card 2022 Download Link released at gate.iitkgp.ac.in, Know How to Download

US President Biden signs 15 executive orders, Reverses various Trump's Policies

China puts sanctions on several officials of Trump administration after Biden becomes president

US Lawmakers certify Joe Biden as winner of Presidential election, clear inauguration on 20 January

US Capitol Updates: Trump finally pledges an orderly transfer of power to Biden

Biden will raise Kashmir issue with India if elected: Blinken, his foreign policy advisor

Memes trolling Crude Oil prices after dumping below Zero for the first time

Rudhran Movie: Release Date, Plot, Cast & Crew, Poster, Trailer & More Details

Ponniyin Selvan 2: Sequel, Release Date, Star Cast, Makers, Plot, Trailer & More

Thuinivu Box Office Collection Day 1: Ajith Kumar’s Film Made A Grand Opening At The BO

Varisu Box Office Collection Day 1: Prediction, Hit or Flop, Advance Booking, Budget, Makers & More

Varisu- Release Date, Trailer Release Date, Premiere, Star Cast & What's New?

Laththi: Release Date, Storyline, Star Cast, Trailer, Makers & More Details

Allahabad High Court RO, ARO Answer Key 2021 Out @recruitment.nta.nic.in! Raise Objections Till 16 Jan

MP Police Constable Answer Key 2022; Check January 13 Shift 1 & 2 Paper Analysis With Solutions

GETCO Vidyut Sahayak Answer Key 2022 Out, Objections Invited Till 14 Jan, Check Result Date Here

LBS Kerala SET Answer Key 2022 Out @lbsedp.lbscentre.in, Check 9 January Paper 1 & 2 Solutions Here
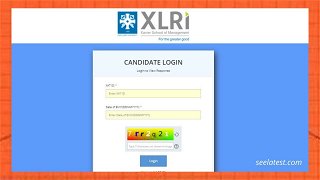
XAT Answer Key 2022 Released at xatonline.in, Check Candidate Response Sheet & Direct Link Here

WB SET Answer Key 2022 Out Soon @wbcsc.org.in, Check 9 Jan General & Subject-specific Paper Analysis Here

The Marvels: Release Date, Starcast & Makers, Storyline, Trailer, Teaser, Budget & More

Extraction 2: OTT Release Date, Sequel, Star Cast & Makers, Plot, Trailer & More

Murder Mystery 2: OTT Release Date, Star Cast, Roles, OTT Platform, Trailers, News & More

Avatar The Way of Water Box Office Collection Day 11- Cameron's Pandora World Eyes Rs 300 Crores In India

Movies Releasing This Christmas 2022- Upcoming Christmas Movies to Watch on OTT

Avatar The Way of Water Box Office Collection Day 8- Cameron's Creation Heading Towards ₹ 200 Crores In India

HIT- The Second Case Box Office Collection Day 5- Adivi Sesh’s Film Starts Impressive At Global Markets

Kantara- OTT Platform, Plot, Box Office Collection, OTT Release Date & More updates are available here

Kantara (Hindi) Box Office Collection Day 14: Kannada Blockbuster Crosses ₹30 Crores in Hindi Belt!

Kantara Box Office Collection Day 19: Rishab Shetty’s Film Going Strong On Weekdays

Kantara Box Office Day 18 Collection: Mystical Film To Cross INR 120 Crores in India!

Kantara: OTT Platform, Release Date, Where To Watch, Streaming Details, TV Rights & More

Shaakuntalam Movie Review: Samantha’s act is upto the mark, though received mixed reviews

Ravanasura Box Office Collection Day 7: Ravi Teja’s Film Seems To Be Pulled Out Of Theatres

Ravanasura Box Office Collection Day 6: Ravi Teja’s Film Remains Steady At The BO

Dasara Box Office Collection Day 13: Nani’s Dasara Sees Steep Drop In BO Collections

Ravanasura Box Office Collection Day 1 & 2: Ravi Teja’s Newly Released Film Has A Thrilling Start

Pushpa: The Rule Movie: Release Date, Announcement, Star Cast, Plot, Teaser, Trailers & More

Haryana Kaushal Rozgar Nigam Registration Begins, Apply Online For CET, Private & Government Jobs @hrex.gov.in

HSSC Fee Refund Notice 2022 For 40 Cancelled Recruitments Out Soon at hssc.gov.in; Details

RRB NTPC Vacancies Revised; Ex-Servicemen Given 10 Percent Reservation, No Vacancy for PWD

RPF Recruitment 2022 For Constable Fake Or Not? Indian Railways Issues Notification

Balchitrakala Registration 2022 Begins @balchitrakala.com; Apply Online Link, Eligibility, Prize Details Here

UP Laptop Yojana Last Date 2022; Know When Will Registration Close for Free Tabs & Smartphones

Maharashtra Home Minister Anil Deshmukh resigns After Bombay High Court Orders CBI investigation

Despite vaccination drive, COVID-19 cases rise across the country, Maharashtra remains worst hit

Mumbai Police Commissioner Param Bir Singh Transferred, Hemant Nagrale appointed as new DGP

NCB arrests Adam Peter D-Souza with illegal drugs worth ₹ 40 lakh from Khar west, Mumbai

Colleges In Maharashtra to re-open from 15 February with 50% attendance: State Minister Uday Samant

Who Will be the Next CM of Maharashtra % of Chances- Rope is in NCP’s Hand

Honsla Rakh Box Office Collection Day 5: Shehnaaz Gill & Diljit's On-Screen Chemistry Dominates The Box Office

Qismat 2 Box Office Collection Day 5: Ammy Virk & Sargun Mehta Starrer Passes Weekday Litmus Test

Balbir Singh Senior Dies! 3 Times Olympic Gold Medalist Hockey Legend passes away at 95

Air Force Mig29 fighter jet crashed in Punjab, IAF sources

Punjab Police ASI dragged on Car bonnet, tried to stop vehicle amid Lockdown

Punjab announces two weeks curfew, lockdown will be lifted from 7-11AM daily

Sher Bagga: OTT Release Date, Time, Platform, Cast, Story, Where To Watch & More

Bajre Da Sitta: Cast, Story, Release Date, Budget, Director, Trailer & More Details

Saunkan Saunkne Day 8 Box Office Collection: The Comedy-Drama Genre Continues To Thrive

Saunkan Saunkne Box Office Collection Day 7: Punjabi Comedy Film Continues Its Successful Run

Saunkan Saunkne Box Office Collection Day 6: Ammy Virk Starrer Leading Punjabi Box Office

Teeja Punjab Box Office Collection Day 2: Nimrat Khaira Starrer Gets Lukewarm Response

Prodigy Finance Brings the Most Accessible Education Loans - A Great Alternative to Traditional Student Funding

How to Get into a Top Engineering College in the United States and Qualify for an Education Loan

Idduki Govt Engineering College Student Stabbed To Death, CM Condemns, Know What's Happened So Far

KVS Class 1 Admission 2022-23 Starting Soon @kvsangathan.nic.in, Check Application Dates, Eligibility, Documents & More

Delhi Nursery Admissions 2022 Last Date Extended For Two Weeks, Announces Education Minister Sisodia

COVID Vaccine Certificate By Name @cowin.gov.in, Know How to Download Universal Pass & Make Corrections

10 Best eCommerce Website Builders In 2022: Made-In-India Platform Also In The List!

MIB Advisory Lost in Legal Ambiguity of Skill vs Chance Gaming

How To Transfer WhatsApp Data From Android To Apple iPhone? Here's Is The Step-By-Step Process

Top 10 Website Builders Of India: These Are Best Website Builders of 2022 In India

Major Media Websites- New York Times, CNN, Bloomberg & Guardian Go Down after Technical Glitch

YouTube and Gmail Crash: How, when and where the 'Google Server' down observed? Details

Thuramukham Release Date, Star Cast, Trailer, Plot, Genre & Everything We Know

Kaapa Release Date, Star Cast, Poster, Trailer, Plot, Genre, Makers & More

Monster Box Office Collection Day 9: Mohanlal Film Completely Falls Flat!

King of Kotha: Cast, Story, Release Date, Director, Budget, Trailer, & More

Kaduva OTT Release Date: Prithviraj Sukumaran Starrer In Trouble Amid Legal Concerns

777 Charlie Box Office Collection Day 3: Gets A Blistering Opening In Karnataka

US blames Taliban for breaking peace agreement : Report

US Navy's Theodore Roosevelt of 7th Fleet entered the South China Sea to conduct routine operations

TIME Magazine declares US Elect Joe Biden, Kamala Harris as 'Persons of Year- 2020' on Cover Page

Ayodhya Ram Mandir Celebration in USA: Indian Community members chant 'Jai Shree Ram' in Washington

Statue of Mahatma Gandhi Vadalised outside Indian Embassy in US, Ambassador Ken Juster apologies

HSSC Police Constable Result 2021 Out Soon @hssc.gov.in; Check Expected Cut-off

DU Special Cut off 2021 Out Today @du.ac.in; Check College-Wise List, Vacant Seats Here

DHE Haryana PG Admissions 2021; First Merit List Out on 2nd November; Required Documents & More

RRB NTPC CBT 1 Cut off 2021; Zone-Wise Expected Cutoff & General, OBC, SC, ST Safe Score Explained

DU First Cut-off 2021 (Joint) Released @du.ac.in; Hansraj, Hindu, SRCC Among Colleges Set 100% For Top-Courses

Delhi University 1st Cut off 2021; Check College-Wise List, Documents Required & Updates Here

Lucknow University Date Sheet 2021 Out at lkouniv.ac.in, BA, BSc, BCom Semester 3, 5 Exams from 6 Jan
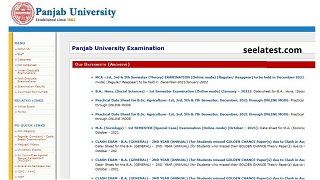
PUCHD Date Sheet 2021 Released For Online UG, PG Exams at puchd.ac.in, Hall Ticket Soon
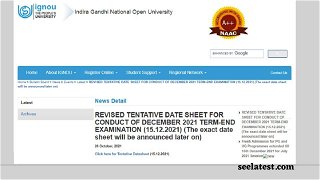
IGNOU New Date Sheet TEE Dec 2021 Released @ignou.ac.in; Hall Ticket Expected On This Date

DU SOL OBE Exams 2021 at Portal solobe.uod.ac.in; Check Date Sheet, Admit Card & Guidelines

IGNOU December 2021 Date Sheet Out @ignou.ac.in; Examination Form Starting Soon

UGC NET Date Sheet 2021; Subject-Wise Exam Dates for Dec & June Cycle Eligibility Test Soon

Sarsenapati Hambirrao Release Date, Cast, Director, Story, Certification & More Details

Ranangan Box Office Collection Day 7: Swwapnil Joshi starrer makes Rs 3.86 crore

Mann Fakiraa Movie Review: Mrinmayee directed Marathi film revolves around tangled Love Story

Farzand Box Office Collection Day 7 : Starring Chinmay Mandlekar

Ranangan Box Office Collection Day 3: Swwapnil Joshi starrer makes Rs 2.12 crore

Vijeta Movie Review & Rating: All about Subodh Bhave's Marathi Sports Drama Film

China imposes Mandarin on Mongolian Population amid protests against removing the local language from schools

Myanmar Coup: Pro-democracy protestors demonstrate in front of Chinese embassy

WHO team in Wuhan reveals that Coronavirus did not emerge from animal sources

US Navy carrier groups conduct military naval exercise in South China sea

80 Chinese gang members arrested for selling fake COVID vaccines: Report

Dozens of drones crash into a building in SW China due to malfunction: Report

Lucknow University Dec 2021 Time Table Released @lkouniv.ac.in, Check BA, BSc, BCom 3rd, 5th Sem Exam Dates

UPBTE Time Table January 2022 Released, Check 1st, 3rd, 5th Semester Scheme Here, Hall Ticket Soon

NMU Dec 2021 Time Table Released at nmu.ac.in; Semester Exam Hall Ticket Soon

Maharashtra SSC & HSC Time Table 2022 Released @mahahsscboard.in; March-April Date Sheet Pdf Here

Dr MGR University Time Table 2021 Out for AHS Diploma, UG Exams @tnmgrmu.ac.in; Hall Ticket on 27 Dec

KSDNEB Time Table 2021 Out at ksdneb.org for December Exams; Download of GNM Hall Ticket Soon

NEET-PG Counselling 2021 Full Schedule Released; Registration, Choice Filling & Allotment Result Dates Here

AACCC Counselling 2021 Registration Starting Soon @aaccc.gov.in, Check Counselling, Seat Allotment Dates Here

NEET PG Counselling 2021 Starting Soon @ nbe.edu.in, Supreme Court Upholds EWS & OBC Reservation Criteria

NEET PG Counselling 2021 Likely To Start Before 6 January, Says IMA President, Schedule Awaited

Doctors' Strike: Demanding NEET-PG Counselling Dates Doctors Meet Health Minister, Outcomes Awaited

MHT CET CAP Round 2 Allotment Result 2021 Today at fe2021.mahacet.org; What Next?

UP Lekhpal Syllabus 2022; Expected Exam Date, Pattern, Previous Year Paper & Marking Scheme Here

UP Board Syllabus for Class 9-12 Reduced by 30%, Model Papers Out at upmsp.edu.in

SEBA Reduces Syllabus for Class 9 & 10 by 40%; Check Revised HSLC Syllabus 2021-22 Here

CBSE introduces 'Coding' and 'Data Science' skill subjects in Schools from session 2021-22

JEE Main 2021 Syllabus for Paper 1 & 2 Released, Here is Maths, Physics, & Chemistry Syllabi pdf

National Test Abhyas: 30 lakh Mock-Test for NEET & JEE students uploaded, MHRD

Constitution Day 2021: Know the Significance, History behind Making of the Indian Constitution

EducationMinisterGoesLive: Board Exams-2021 not to be conducted in Feb-March 2021, AI to be introduced soon

Education Minister Goes Live: Ramesh Pokhriyal to address Teachers on CBSE Exams 2021 at 4 PM

PMI Modi Addresses Aligarh Muslim University on Centenary Ceremony, releases Postage Stamp

PM Narendra Modi honored with US' Highest Award 'Legion of Merit' Award

PM Modi to deliver address at AMU Centenary on 22 Dec, First PM since 1964